The burgeoning operational scale of Amazon’s logistics network has precipitated a notable surge in its associated emissions.
Overview of Amazon’s Shipping Network and its Environmental Impact
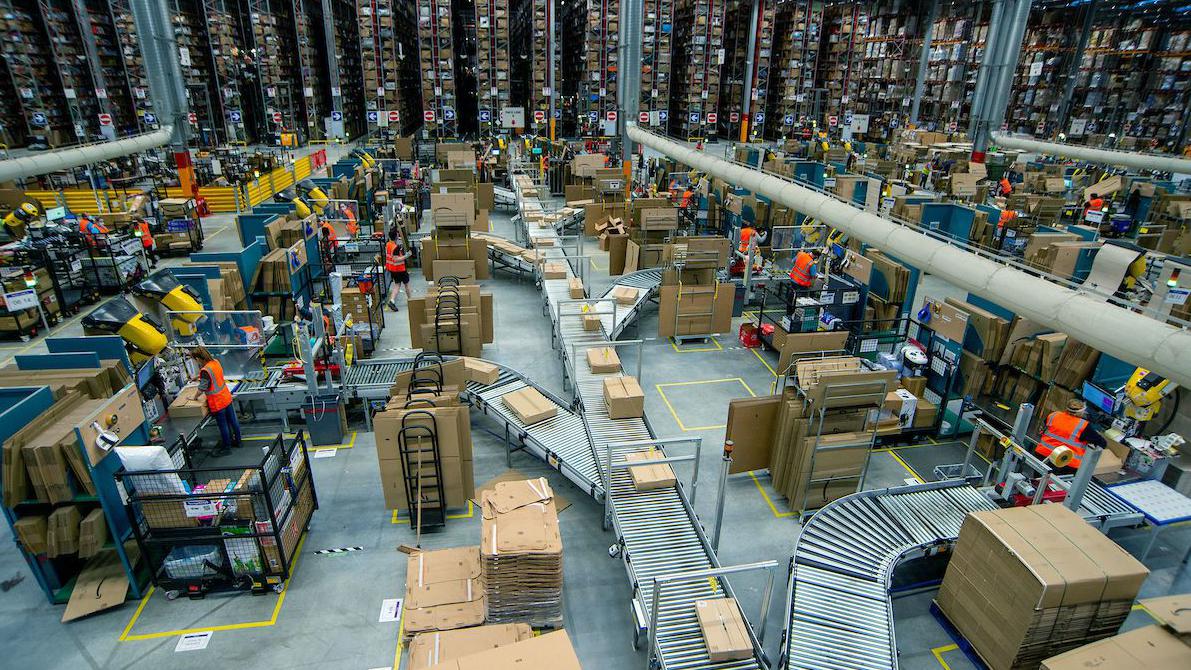
Amazon’s expansive shipping infrastructure encompasses a multifaceted system comprising fulfillment centers, sorting facilities, and a vast transportation network. This intricate web facilitates the movement of goods from vendors to consumers globally, involving diverse modes of transport, including trucking, air freight, and maritime shipping. The environmental implications of this extensive network are substantial, primarily due to the consumption of fossil fuels which drives the majority of its operations. The combustion of these fuels results in significant emissions of greenhouse gases, notably carbon dioxide, which contributes to climate change. Furthermore, the sheer volume of packaging materials utilized in the shipping process adds to the environmental burden, generating substantial waste and placing strain on recycling systems. The cumulative impact of these factors underscores the urgent need for mitigation strategies to address the escalating environmental consequences of Amazon’s logistical activities. The environmental impact is not solely limited to carbon emissions, but also includes impacts on local ecosystems and communities due to the large scale of operations.
Analysis of Contributing Factors to Emissions Growth
Several key factors contribute to the escalating emissions associated with Amazon’s logistics operations.
Expansion of Delivery Infrastructure and Increased Order Volume
The exponential growth of Amazon’s delivery infrastructure, characterized by the proliferation of fulfillment centers and distribution hubs, is a primary driver of its escalating emissions. This expansion, designed to meet the ever-increasing consumer demand for rapid delivery, necessitates extensive transportation networks, thereby amplifying the consumption of fossil fuels. The increased volume of orders processed daily further exacerbates this situation, as each package requires transportation, leading to a proportional increase in emissions. The strategic placement of fulfillment centers in proximity to population centers, while enhancing delivery speed, also contributes to higher emissions due to the cumulative effect of numerous short-haul trips. The implementation of expedited delivery options, such as same-day and next-day services, adds another layer of complexity, requiring more frequent and often less efficient transportation routes. The combination of infrastructure expansion and order volume intensifies the environmental impact of Amazon’s logistics, making it crucial to address these factors in developing sustainable solutions. Furthermore, the growth in international shipping contributes significantly to the overall emissions due to the distances involved and the use of less efficient transportation methods.
Addressing the escalating environmental impact of Amazon’s logistics operations necessitates the implementation of comprehensive mitigation strategies and the adoption of sustainable practices. A multi-faceted approach is crucial, encompassing both operational adjustments and technological innovations. Transitioning to a greater reliance on renewable energy sources for powering fulfillment centers and transportation fleets is paramount. This includes the adoption of electric vehicles for last-mile delivery and investing in renewable energy infrastructure, such as solar and wind power. Optimizing delivery routes and consolidating shipments can significantly reduce transportation-related emissions. Furthermore, promoting the use of more sustainable packaging materials and minimizing packaging waste is essential. Encouraging consumer awareness and participation in sustainable practices, such as opting for slower shipping options and consolidating purchases, can also contribute to reducing the overall environmental footprint. Collaboration with policymakers and stakeholders is vital to developing and implementing effective regulations and standards that promote sustainable logistics. A commitment to transparency and accountability in reporting emissions data is crucial for monitoring progress and ensuring continuous improvement. The integration of advanced technologies, including AI-powered route optimization and predictive analytics, can enhance efficiency and minimize waste in the long term.